Arabia

Transforming Healthcare in Saudi Arabia
Introduction to Vision 2030
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 represents a strategic framework aimed at transforming the nation across various sectors, with a particular emphasis on healthcare. Initiated by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, this ambitious vision outlines several core objectives, ultimately striving to reduce the country’s reliance on oil, diversify the economy, and enhance the quality of life for its citizens. A significant focus of Vision 2030 is the healthcare sector, which is vital for achieving public health and economic stability.
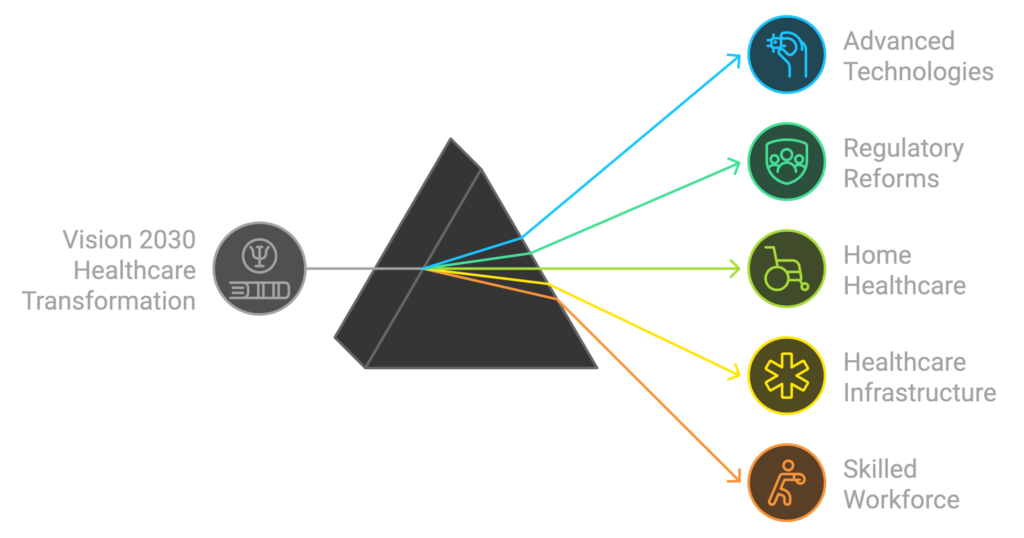
The Vision aims to elevate the standard of healthcare services provided to the population, ensuring more accessible and efficient medical care. It reflects a commitment to improving health outcomes, tackling prevalent diseases, and fostering an environment conducive to innovation in medical practices. Integral to this transformation is the integration of advanced technologies, adherence to global best practices, and the establishment of sustainable healthcare systems. Funding initiatives through medical insurance schemes and private sector involvement are crucial for enhancing home healthcare options, which facilitate personalized care within the comfort of patients’ residences.
Additionally, Vision 2030 addresses the need for regulatory reforms that promote patient rights, enhance the quality of healthcare delivery, and encourage transparency within the system. By prioritizing the development of healthcare infrastructure and the availability of a skilled workforce, Saudi Arabia seeks to build a robust healthcare environment that meets the increasing demands of a growing population.
As the nation embraces this transformative period, the focus on home healthcare presents an opportunity to improve patient outcomes by offering services that are tailored to individual needs. Overall, the healthcare initiative within Vision 2030 illustrates Saudi Arabia’s commitment to a healthier future, setting the stage for substantial progress in medical care and access across the kingdom.
Current State of Healthcare in KSA
Prior to the implementation of Vision 2030, healthcare in Saudi Arabia faced numerous challenges that hindered its efficiency and effectiveness.
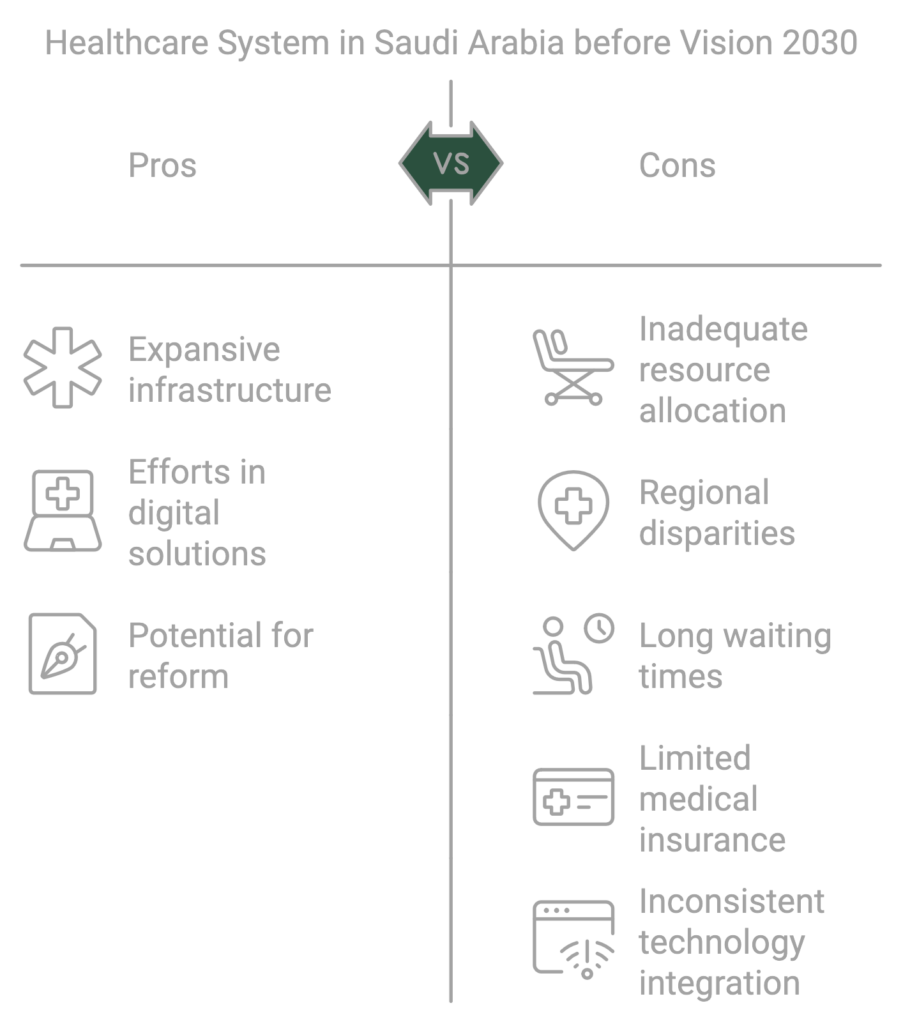
The existing healthcare infrastructure, though expansive, was often characterized by inadequate resource allocation, resulting in disparities in service delivery across different regions. Many rural areas struggled with a lack of essential medical facilities and personnel, creating barriers to accessing timely healthcare services. As a consequence, the nation grappled with variations in patient outcomes, where urban populations enjoyed better healthcare quality compared to their rural counterparts.
Furthermore, the heavily public healthcare system strained under the demand of a growing population. With the majority of the population relying on public hospitals for their health needs, long waiting times and insufficient patient care became common complaints. The reliance on medical insurance to bridge the gaps in the public system was limited, as only a segment of the population could access comprehensive coverage. Most citizens faced financial burdens when seeking private healthcare options, highlighting the essential need for reforms in medical insurance policies.
Additionally, the integration of technology and telemedicine into the healthcare framework remained inconsistent prior to Vision 2030. Although there were attempts to enhance patient engagement through digital solutions, the widespread adoption was lacking. This limited access to vital health information and remote consultations for patients, particularly in underserved areas. These hurdles necessitated a robust reevaluation of the existing healthcare infrastructure, paving the way for strategic initiatives aimed at transforming the overall healthcare landscape in Saudi Arabia.
In light of these challenges, Vision 2030 is set to address the shortcomings of the existing system, focusing on improving healthcare accessibility and enhancing patient outcomes across the nation.
Key Components of Healthcare Transformation
The healthcare transformation initiative in Saudi Arabia, as envisioned in Vision 2030, constitutes a comprehensive strategy designed to enhance the quality of healthcare services across the nation.
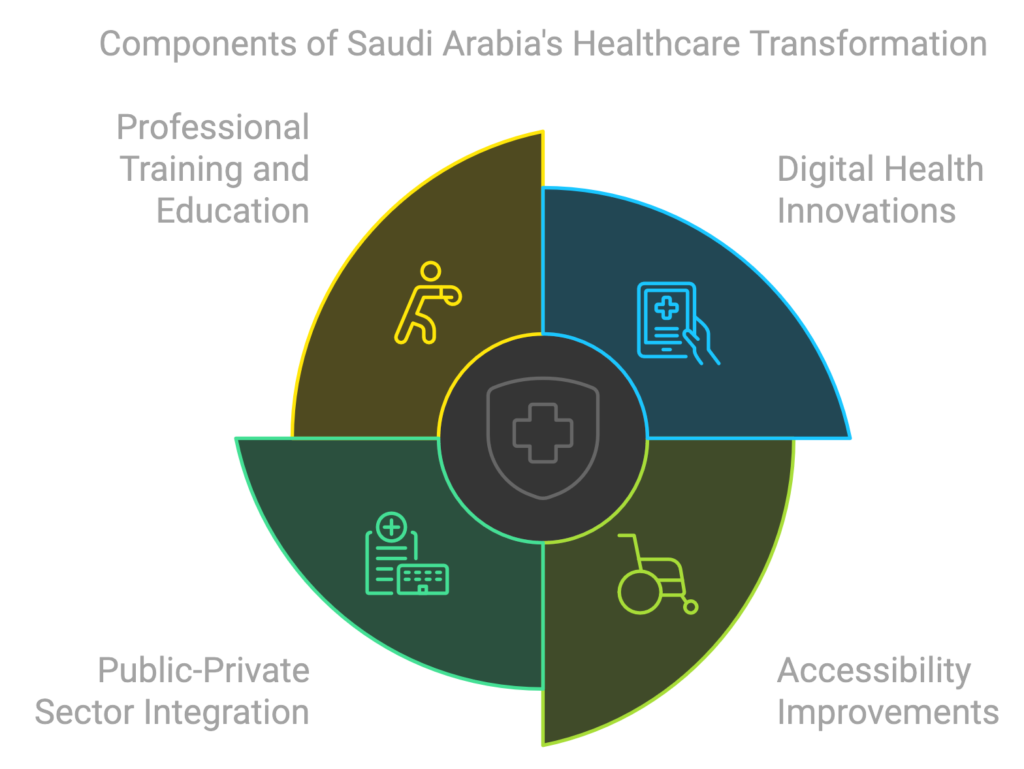
Central to this transformation is the adoption of digital health innovations, which aim to streamline patient care, improve management systems, and facilitate access to medical services. By leveraging technology such as telemedicine and electronic health records, healthcare providers can deliver care more efficiently and effectively. This shift not only enhances patient experience but also fosters a more data-driven approach to healthcare delivery.
Another critical component of the transformation is the focus on improving healthcare accessibility. The Saudi government recognizes the need to cater to diverse population segments, ensuring that medical services are available to all. Initiatives include expanding healthcare infrastructure in rural and underserved areas, thereby bridging the gap between urban and rural healthcare services. This commitment to accessibility is reinforced by policies that promote home healthcare services, enabling patients to receive care in the comfort of their homes, supported by the appropriate medical insurance plans.
Integrating the private and public healthcare sectors is essential to achieving a more cohesive healthcare system. By fostering collaboration between these sectors, resources can be optimized, leading to increased efficiency and improved patient outcomes. This integration also encourages private investment in healthcare facilities and innovations, which are necessary for sustaining growth and improving service delivery.
Lastly, enhancing professional training and education for healthcare professionals plays a pivotal role in this transformation. Continuous professional development ensures that medical personnel are well-equipped with the latest knowledge and skills to provide high-quality care. By investing in education, Saudi Arabia aims to build a robust workforce capable of meeting the evolving demands of its healthcare landscape.
The Role of Technology in Healthcare Transformation
The transformation of healthcare in Saudi Arabia, particularly in the context of Vision 2030, is significantly influenced by the integration of advanced technologies.
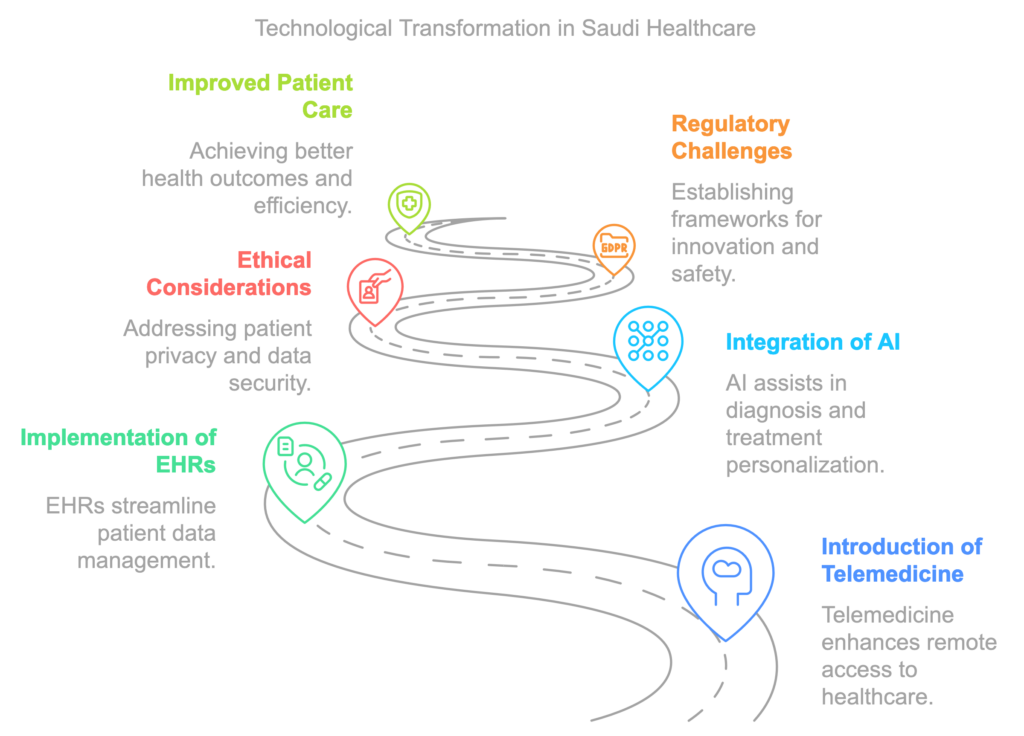
Telemedicine represents one of the most prominent innovations, allowing patients to access medical care remotely, thus enhancing accessibility and convenience. It is particularly advantageous for those living in rural areas, minimizing the need for travel and reducing the burden on healthcare facilities. This shift not only improves patient outcomes but also optimizes the utilization of medical resources.
Moreover, the implementation of electronic health records (EHRs) streamlines patient data management. EHR systems facilitate the aggregation of patient information, making it readily accessible to healthcare providers. This immediacy enhances decision-making processes, improves efficiency, and promotes coordinated care among different healthcare professionals. The historical reliance on paper-based records is diminishing, giving way to a digitally driven infrastructure that supports comprehensive home healthcare solutions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications further illustrate the profound impact of technology on healthcare. By processing vast amounts of data, AI can assist in diagnosing medical conditions, predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans. The implementation of machine learning algorithms is transforming diagnostics and therapeutic strategies, providing clinicians with unprecedented levels of support in their decision-making. However, the integration of such technologies prompts critical ethical considerations, particularly concerning patient privacy and data security.
Additionally, regulatory challenges arise as policymakers must establish frameworks that support innovation while ensuring that patient safety and confidentiality are maintained. Balancing the rapid pace of technological advancements with ethical principles and regulatory compliance is vital to successfully navigating the evolving landscape of home healthcare in Saudi Arabia. The journey toward a technologically advanced healthcare system is ongoing, but it promises improved patient care and a more efficient healthcare delivery model.
Public-Private Partnerships in Healthcare
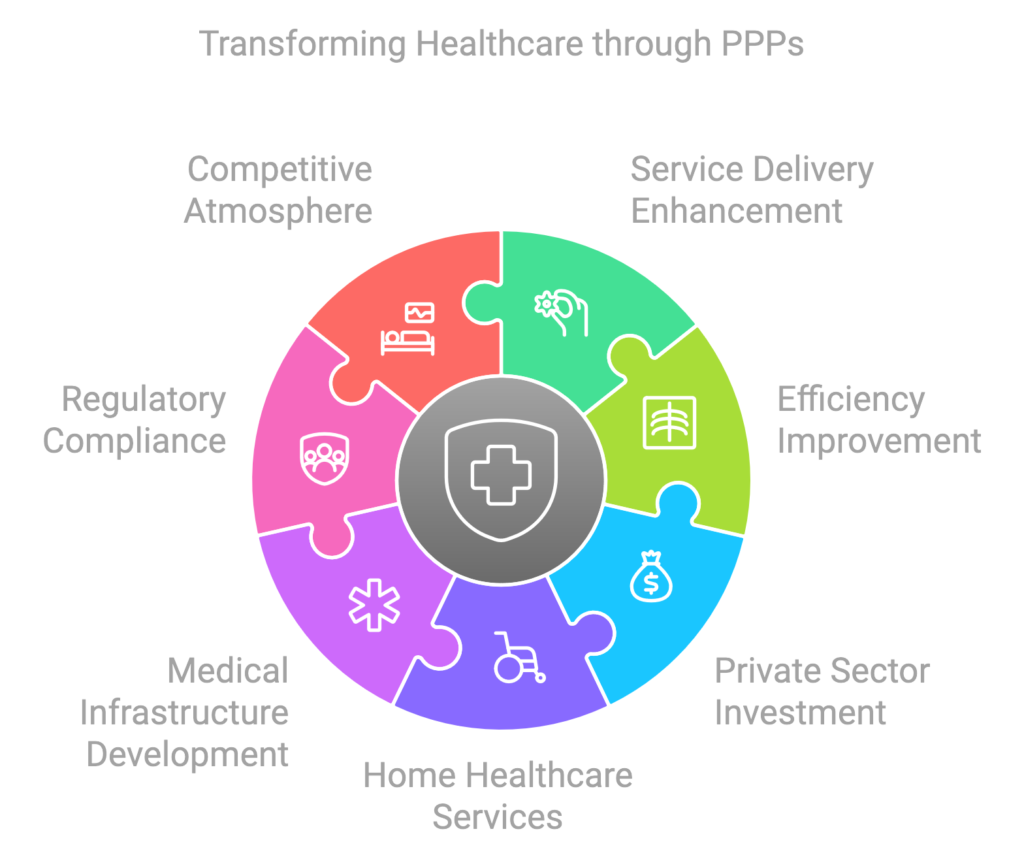
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) have emerged as fundamental components in the transformation of healthcare in Saudi Arabia, significantly aligning with the goals of Vision 2030. These collaborations aim to enhance service delivery, improve efficiency, and leverage private sector investment, ultimately benefiting the healthcare landscape. The involvement of private entities in healthcare provision not only fosters innovation but also addresses the increasing demand for quality medical services amidst a growing population.
One of the exemplary projects showcasing the success of PPPs in Saudi Arabia is the collaboration between the Ministry of Health and private hospitals for providing home healthcare services. This initiative has streamlined access to essential medical attention for individuals recovering from surgeries or managing chronic illnesses in the comfort of their homes. By integrating home healthcare services into the existing medical insurance framework, patients can now receive care without the burdens of excessive out-of-pocket expenses. This is a significant leap forward in making medical services more accessible and accommodating to patient needs.
Additionally, PPPs have facilitated investments in medical infrastructure through joint ventures that build hospitals and clinics equipped with state-of-the-art technology. These partnerships ensure that both public and private sectors share the risks and rewards, fostering a more balanced healthcare environment. As a result, the quality of service has improved markedly, with private players introducing more efficient practices while maintaining compliance with the regulatory standards set by the government. Furthermore, these partnerships encourage a competitive atmosphere, leading to enhanced patient experiences and clinical outcomes.
In conclusion, the role of public-private partnerships in healthcare reform is increasingly pivotal in Saudi Arabia. As these collaborations continue to flourish, it is expected that they will play a crucial part in achieving the broader objectives stated in Vision 2030, particularly concerning investments in healthcare that yield tangible improvements in service delivery and accessibility for all citizens.
Health Sector Transformation Program
With a focus on improving access to healthcare, modernizing facilities and equipment, and enhancing the role of private sector investment, Saudi Arabia’s healthcare system is undergoing a transformation to meet the needs of every member of society.
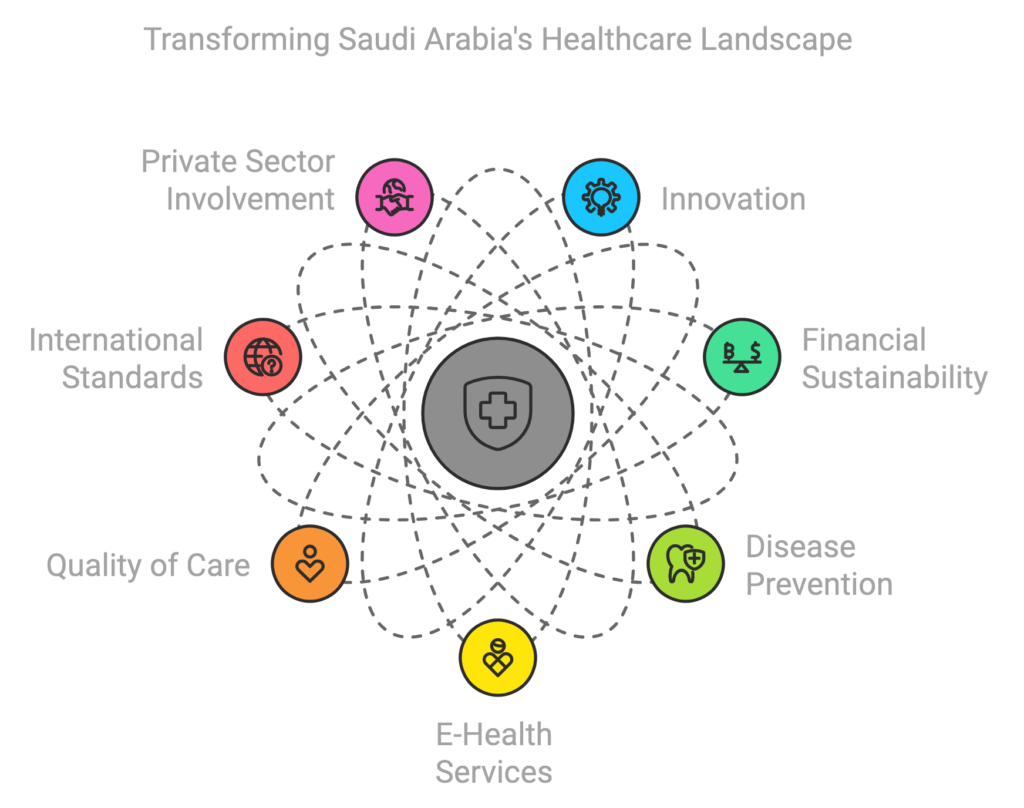
The Healthcare Sector Transformation Program is transforming the Kingdom’s healthcare system to be more comprehensive, effective, and integrated than ever before. This enhanced system prioritizes innovation, financial sustainability, and disease prevention while improving access to healthcare. It also focuses on expanding e-health services and digital solutions, improving the quality of care, and adhering to international standards.
The Program’s strong cooperation and integration with government entities enabled Saudi Arabia to swiftly and effectively address the COVID-19 pandemic. Through the use of mobile applications, streamlined vaccine protocols, and increased access to medical services, the Kingdom was a global model of excellence in successfully mitigating the spread of the virus.
From remote surgeries guided by top physicians to virtual consultations resulting in seamless prescriptions, the Kingdom is leading the charge in utilizing technology to revolutionize the delivery of healthcare services with ease and efficiency. Launched in 2022, the SEHA Virtual Hospital is the largest of its kind globally, connecting over 150 hospitals with more than 30 specialized health services.
The Program is also improving public health and preventing diseases. This is a crucial area of investment for the health and productivity of individuals and communities, as prevention is often more cost effective than illness and injury treatment.
The private sector is vital in supporting the Kingdom’s efforts to achieve its national health goals, ensuring everyone has access to high-quality healthcare.
Key Objectives of Healthcare Transformation
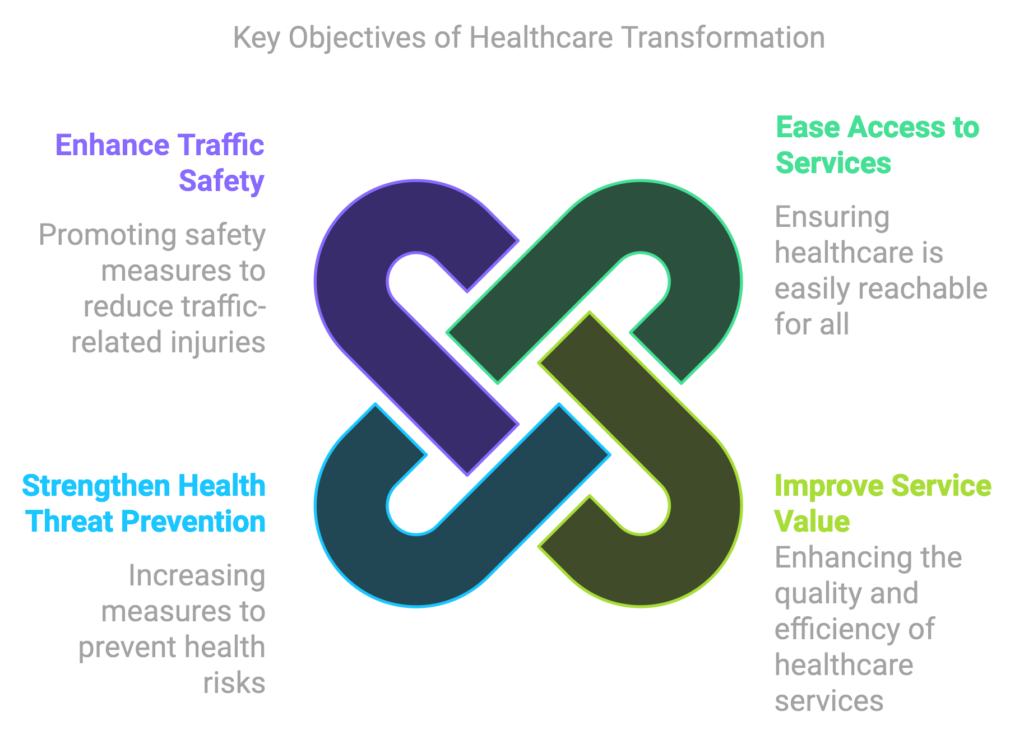
Objectives
- Ease the access to healthcare services
- Improve value of healthcare services
- Strengthen prevention against health threats
- Enhance traffic safety
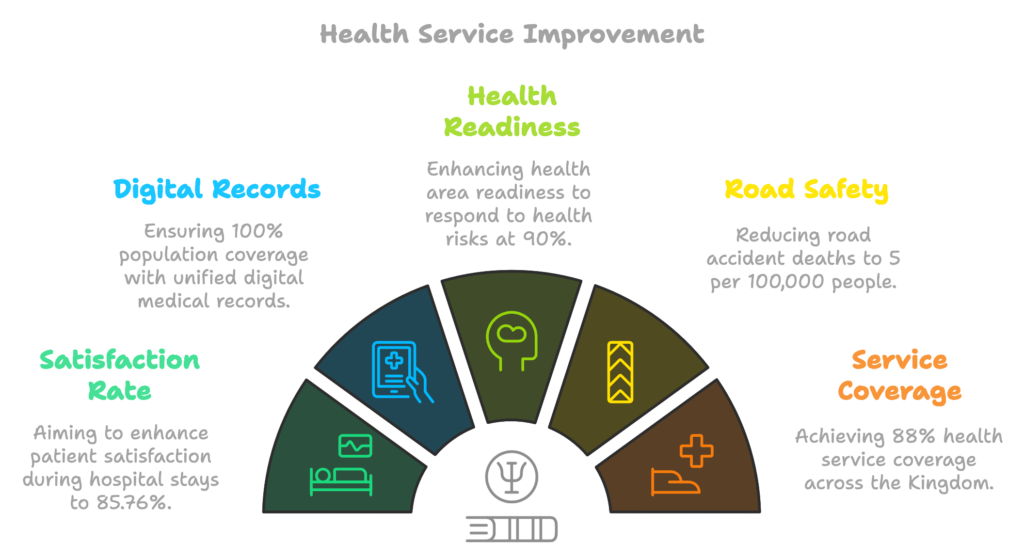
Healthcare improvement targets
85.76%
Increase the beneficiary satisfaction rate with health service experiences during hospitalization to 85.76%.
100%
Ensure the dissemination of the unified digital medical record to include 100% of the population.
90%
Enhance the readiness of health areas to effectively respond to health risks, aiming for a readiness rate of 90%.
5
Reduce the average number of deaths from road accidents to 5 per 100,000 people.
88%
Achieve a target of 88% coverage of health services across the Kingdom, including peripheral areas and population centers, by 2023 AD.
Groundbreaking Health Initiatives Developed
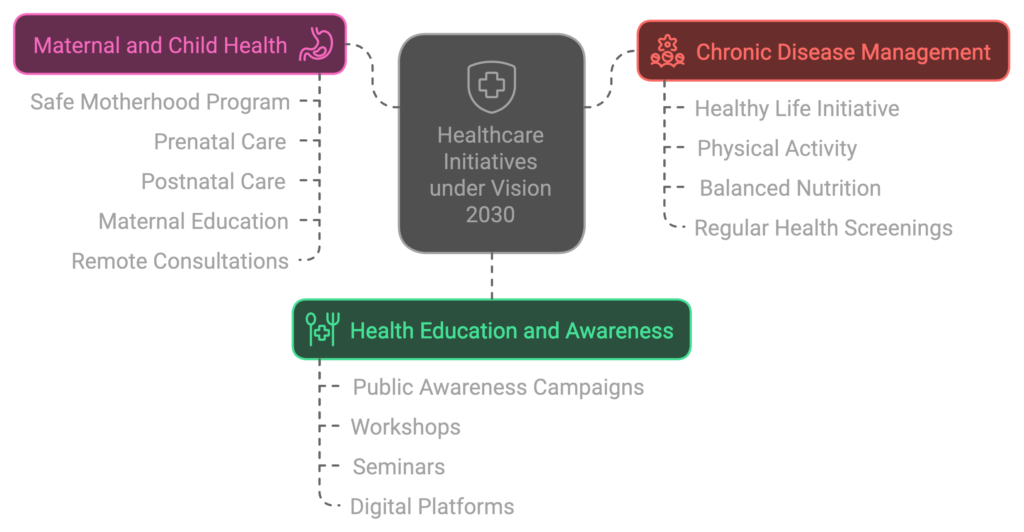
Under the framework of Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia has embarked on a transformative journey to enhance its healthcare system. A key focus has been the introduction of groundbreaking health initiatives that aim to address prevalent health challenges such as chronic diseases, maternal and child health, and the importance of health education and awareness. These initiatives are designed not only to significantly improve the quality of life for its citizens but also to ensure that medical insurance becomes more accessible and relevant to different population segments.
One prominent program is the “Healthy Life” initiative, which emphasizes the prevention and management of chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. Through this program, the Ministry of Health collaborates with various stakeholders to facilitate community-based interventions aimed at promoting physical activity, balanced nutrition, and regular health screenings. By empowering individuals with knowledge and resources, the initiative seeks to reduce the burden of chronic illness while enhancing overall home healthcare services across the nation.
Moreover, substantial investments have been made in improving maternal and child health. The “Safe Motherhood” program is an illustrative example, which offers comprehensive healthcare services for expecting mothers and their infants. This initiative not only focuses on prenatal and postnatal care but also on maternal education to foster better health practices within the family. With the integration of modern technology, healthcare providers can offer remote consultations, making healthcare more approachable for many families, especially in rural areas.
In addition, the Ministry of Health has launched various health education and awareness campaigns targeting diverse audiences to promote preventive healthcare. These initiatives aim to raise public awareness about health risks, available medical services, and the vital role of early detection and treatment. The engagement of citizens through workshops, seminars, and digital platforms signifies a shift towards a more informed society capable of making better health choices.
Impact on Health Workforce and Education
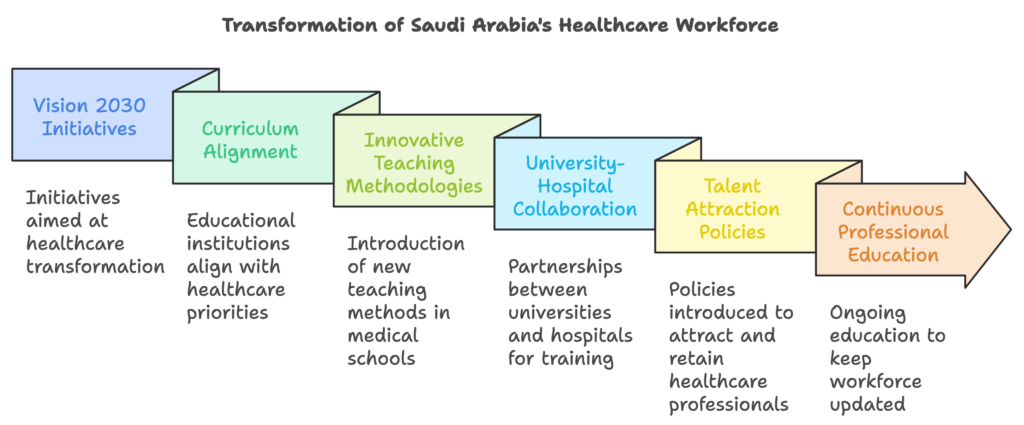
The transformative vision set forth by Vision 2030 in Saudi Arabia has significantly influenced the health workforce and education within the country. Recognizing the critical role of healthcare professionals in delivering quality services, the government has implemented various initiatives aimed at enhancing medical education and training programs. These reforms are essential for developing a skilled workforce capable of meeting the growing demands of an evolving healthcare system, particularly in the context of increasing home healthcare services.
To begin with, educational institutions are now required to align their curriculum with national healthcare priorities. This alignment ensures that future healthcare professionals are well-equipped with contemporary knowledge and practical skills. The introduction of innovative teaching methodologies in medical schools, coupled with advanced simulation techniques, promotes an experiential learning environment that better prepares graduates for real-world challenges. Furthermore, collaborative efforts between universities and healthcare facilities are fostering a robust ecosystem for clinical training and research, which is vital for improving the competencies of healthcare providers across the board.
Another significant shift is reflected in the initiatives aimed at attracting and retaining talent within the medical field. The Saudi government has introduced policies that offer competitive salaries, benefits, and professional development opportunities to healthcare workers. Such policies not only incentivize professionals to pursue careers in healthcare but also promote long-term engagement within the sector. The emphasis on continuous professional education further aids in maintaining a workforce that is well-versed in the latest medical advancements, bolstering the quality of care provided to patients. These efforts ultimately contribute to a more resilient healthcare system that can effectively address both existing and emerging health challenges.
Future Prospects and Goals
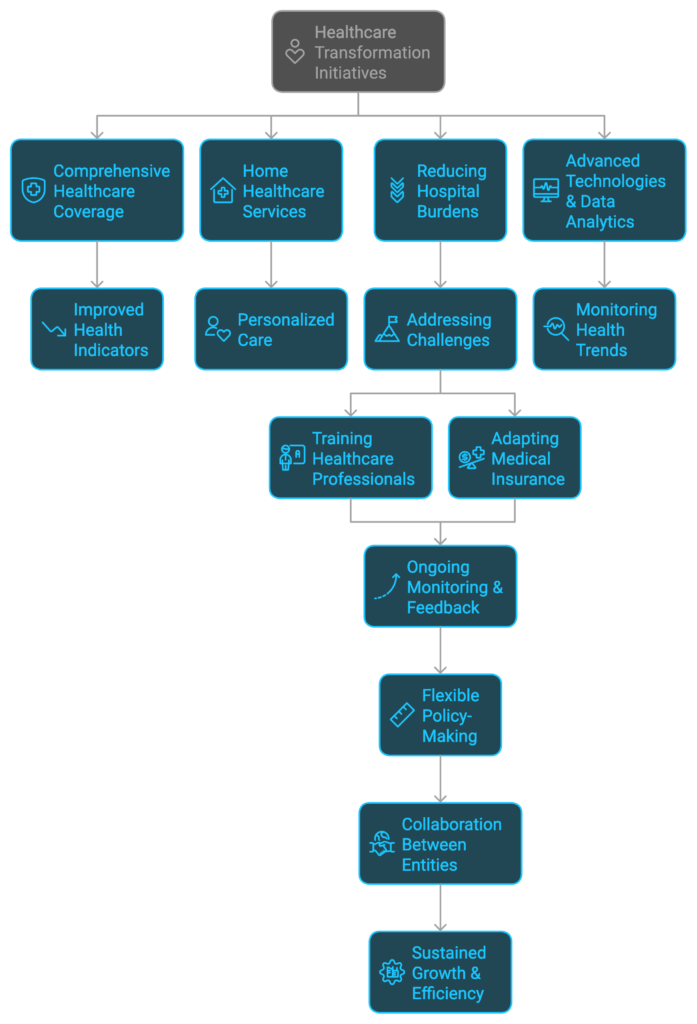
The healthcare transformation initiatives under Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 are designed to foster a robust and accessible healthcare system, focusing on enhancing the overall quality of care provided to citizens. One of the primary long-term goals is to achieve comprehensive healthcare coverage, which includes home healthcare services for patients with varying needs. This approach will not only ensure that individuals receive necessary medical attention but also alleviate the burden on hospital infrastructures. The integration of home healthcare into the medical insurance framework is critical, as it presents opportunities for more personalized care and reduces costs associated with hospital admissions.
Moreover, the anticipated outcomes extend beyond immediate healthcare delivery. As the healthcare system evolves, it is expected that key health indicators, such as life expectancy and disease prevalence, will see significant improvement. The integration of advanced technologies and data analytics will play a vital role in monitoring health trends, allowing for proactive measures tailored to the population’s needs. Despite the optimistic outlook, challenges may arise, including the need for extensive training to ensure healthcare professionals are adept at delivering home healthcare services and adapting to the changing landscape of medical insurance.
Ongoing monitoring and feedback mechanisms will be essential in navigating these challenges, allowing the authorities to make necessary adjustments to the implemented strategies. Flexibility in policy-making will enable the government to respond effectively to emerging trends and health crises while maintaining a commitment to innovation in the healthcare sector. By fostering collaboration between public and private entities, the transformation initiatives are anticipated to sustain growth, ensuring healthcare remains accessible and efficient for all citizens of Saudi Arabia.
Conclusion: A New Era for Healthcare in Saudi Arabia
The healthcare sector in Saudi Arabia is undergoing a remarkable transformation, spurred by the Vision 2030 initiative, which aims to enhance the quality of life and services for its citizens. This comprehensive plan has laid the groundwork for significant changes in various aspects of healthcare, including access to home healthcare services and the optimization of medical insurance frameworks. As the nation moves forward, it becomes increasingly vital for all stakeholders—government agencies, healthcare providers, and the community—to collaborate and contribute to the ongoing evolution of this critical sector.
One of the major developments stemming from Vision 2030 is the emphasis on privatization and public-private partnerships, which are essential for improving healthcare delivery and patient outcomes. This shift not only increases efficiency but also encourages the integration of innovative technologies and services, making healthcare more accessible and patient-centric. Furthermore, the expansion of preventive care initiatives has become a priority, promoting health awareness and reducing the burden of chronic diseases on the healthcare system.
Another significant transformation involves the enhancement of medical insurance policies that cater to a wider segment of the population. By improving the coverage options and making health services more affordable, the government aims to ensure a higher standard of care. The focus on home healthcare services allows patients to receive treatment in familiar environments, further aligning with the modern patient-oriented perspective of care delivery.
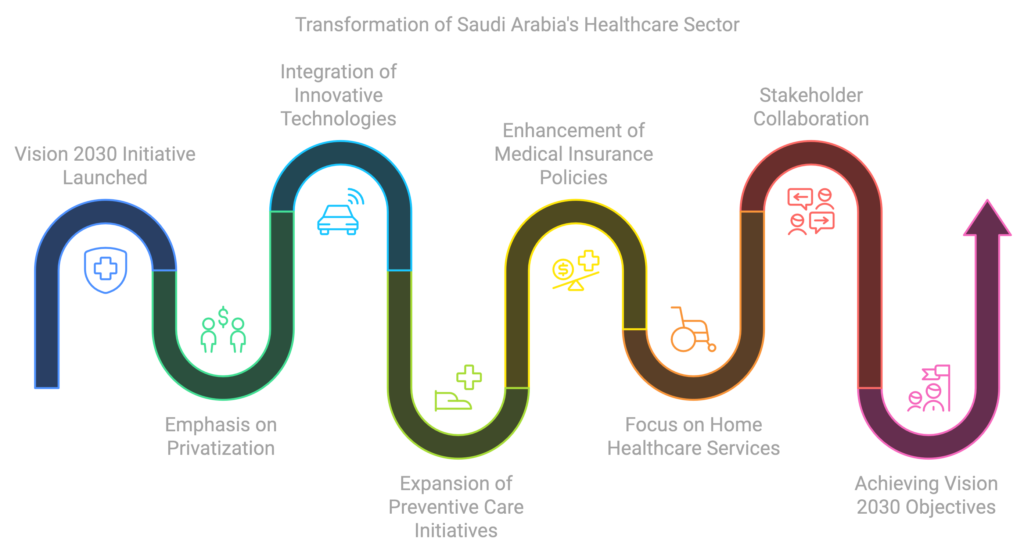
As Saudi Arabia continues to navigate this new era of healthcare, it is evident that the synergistic efforts of all stakeholders are crucial for realizing the Vision 2030 objectives. The journey ahead is promising but requires sustained commitment, innovation, and cooperation to build a sustainable and efficient healthcare system that meets the needs of its growing population.
